Why Stopping the Bleed is Important ?
Proportion of Casualties in the United States
According to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), millions of people are injured each year due to various accidents, many of which involve severe bleeding. Severe bleeding is one of the leading causes of death from accidents, particularly in traumatic events. Even in areas with abundant medical resources, deaths caused by bleeding remain a serious public health issue. Data shows that timely and effective bleeding control can significantly reduce trauma-related mortality rates.

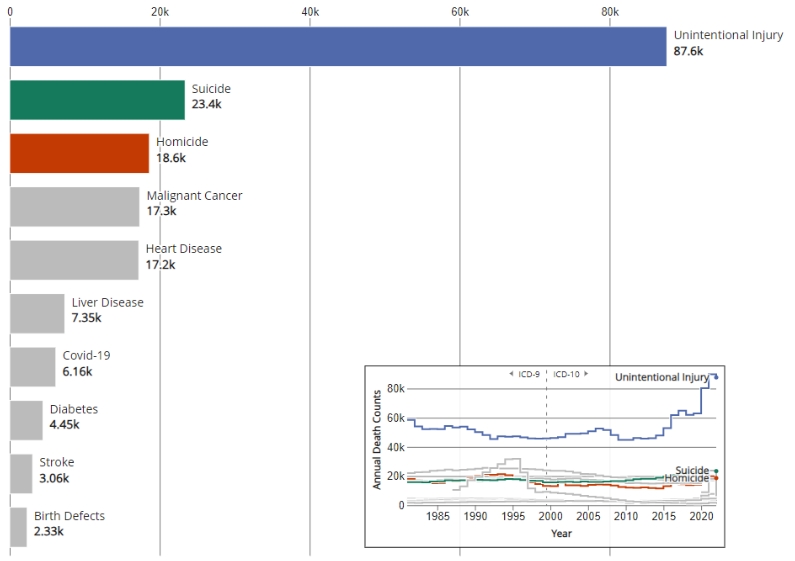
Top Ten Leading Causes of Death in the U.S. for Ages 1-44 from 2022
1.Unintentional injuries are the leading cause of death for Americans aged 1-44 years pd.
2.Unintentional injuries include opioid overdoses (unintentional poisoning), motor vehicle crashes, and unintentional falls.
3.Suicide is now the 2nd leading cause of death for this 1-44 age group, and numbers of suicides continue to rise.
4.Homicide remains in the top 5 leading causes of death for the 1-44 age group.
Annual Incidents of Severe Bleeding:
According to the CDC, unintentional injuries, including severe bleeding, are a leading cause of death. In 2022, there were over 200,000 deaths from unintentional injuries, a significant portion of which involved severe bleeding (CDC) .
Traffic Accidents:
In 2019, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) reported that there were 36,096 fatalities from motor vehicle crashes. Of these, it is estimated that about 10-20% of deaths were due to severe bleeding before reaching the hospital (USC Center for Health Journalism).
Preventable Trauma Deaths:
Studies have shown that approximately 30% of trauma victims could potentially survive with timely and effective medical care, including bleeding control. For instance, research in Harris County, Texas, found that 36% of trauma deaths were from potentially survivable wounds, and uncontrolled bleeding was a significant cause (USC Center for Health Journalism).
Military vs. Civilian Care:
Military studies have demonstrated that proper bleeding control measures, such as the use of tourniquets and timely blood transfusions, significantly reduce mortality rates. For example, during the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq, mortality rates for troops fell by nearly 50% due to improved bleeding control techniques (USC Center for Health Journalism).

Conclusion
Effective bleeding control measures can save countless lives. According to CDC data, millions of people are injured annually in the United States due to various accidents, and many deaths are attributed to severe bleeding. Unintentional injuries are a leading cause of death in the U.S., with over 200,000 fatalities in 2022, a significant portion involving severe bleeding. These statistics demonstrate that timely and effective bleeding control could prevent many deaths resulting from excessive blood loss. For instance, thousands of Americans are injured in traffic accidents each year, and approximately 10-20% of these fatalities are due to the inability to stop bleeding in time.
Military medical research has shown that appropriate bleeding control measures significantly reduce mortality rates on the battlefield. During the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq, improved bleeding control techniques led to nearly a 50% reduction in mortality rates among troops. This indicates that applying these proven military bleeding control methods to civilian emergency medical systems could dramatically decrease trauma-related deaths (USC Center for Health Journalism).
learning and promoting bleeding control techniques are crucial for improving public health. As individuals, we should actively participate in public health campaigns like "Stop the Bleed," learning basic first aid skills to save lives in emergencies. These skills not only benefit individuals but also positively impact families, communities, and society at large. Every second counts in critical situations, and timely bleeding control measures are undeniably vital for saving lives. Let us work together to ensure more people can take the right actions in critical moments, thereby protecting more lives.
Where to Participate in Stop the Bleed Activities or Courses
To participate in "Stop the Bleed" training courses, you can find resources and training centers through the following:
- Stop the Bleed Official Website: (link)
Visit the Stop the Bleed website to find information about upcoming courses, training materials, and local events. They offer both in-person and online training options. - Local Hospitals and Medical Centers:
Many hospitals and medical centers offer "Stop the Bleed" courses. Check with your local hospital’s community outreach or education department for available courses. - American Red Cross:(link)
The American Red Cross often includes bleeding control techniques in their first aid courses. Visit the American Red Cross website to find courses near you. - Community Centers and Schools:
Some community centers and educational institutions offer "Stop the Bleed" training as part of their public health initiatives. Check with local community centers or school districts for available programs. - Fire Departments and Emergency Services:
Local fire departments and emergency medical services (EMS) often host training sessions for the public. Contact your local fire department or EMS for information on scheduled courses.
Participating in these training sessions equips individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to effectively control bleeding in emergency situations, potentially saving lives.

The Importance of Wound Simulation Training
Wound simulation training holds significant importance in emergency response and medical training. Here are several key reasons explaining its importance:
Wearable Wound Kit(link)
The Wearable Wound Kit is an innovative training tool designed for realistic and effective bleeding control practice. This kit includes wearable devices that simulate various types of wounds, each capable of bleeding in a controlled manner, allowing trainees to practice their hemorrhage control skills in a lifelike scenario. The wounds are designed to mimic real-life injuries, ensuring that the training closely aligns with actual bleeding control processes and logic.
The kit includes different types of wounds, such as lacerations, punctures, and deep cuts, each with its own specific bleeding pattern and severity. This variety enables trainees to experience a wide range of situations, enhancing their ability to respond effectively to different types of bleeding injuries. The realistic nature of the wounds helps to build confidence and competence in applying direct pressure, using tourniquets, and performing wound packing—crucial skills in emergency medical situations.
One of the key features of the Wearable Wound Kit is its ability to simulate real-time bleeding, which provides immediate feedback on the effectiveness of the applied techniques. This immediate feedback loop is essential for learning and correcting mistakes, ensuring that trainees can refine their skills through practice. Moreover, the kit is designed to be worn by both mannequins and live actors, allowing for versatile training scenarios that can include both individual practice and team-based emergency response drills.
By providing a hands-on, immersive training experience, the Wearable Wound Kit plays a crucial role in preparing individuals for real-life emergencies. Whether used in medical schools, military training, or community first aid courses, this kit enhances the preparedness of trainees, ultimately contributing to better outcomes in actual bleeding emergencies. Through repeated practice with realistic wound simulations, users of the Wearable Wound Kit can develop the confidence and skills necessary to save lives when it matters most.


More content
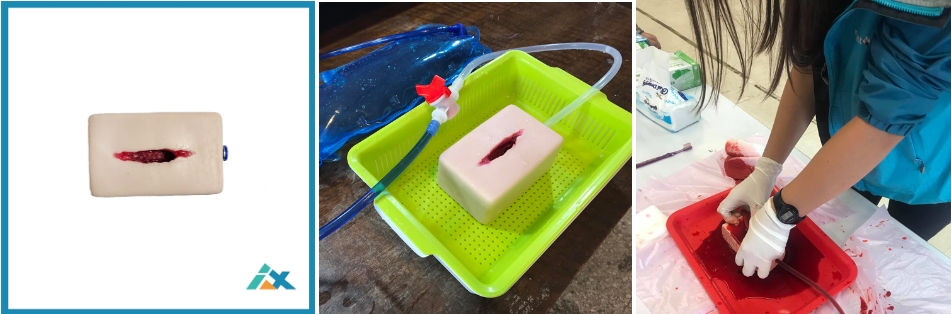
Packing Wound Training(link)
Our packing wound training equipment is distinct from other brands due to the presence of three bleeding points inside the wound. This design prevents trainees from simply using their fingers to block the wound, ensuring they must thoroughly pack the wound with gauze to achieve effective hemostasis. This approach requires more precise and complete action from the trainees, ensuring they develop the capability to control bleeding effectively in real-life scenarios. This realistic training method not only enhances the technical skills of the trainees but also boosts their confidence and response abilities in emergency situations, allowing them to better protect lives during actual rescue operations. Through this rigorous training, trainees can master the true technique of wound packing rather than relying on simple, temporary measures.

More content
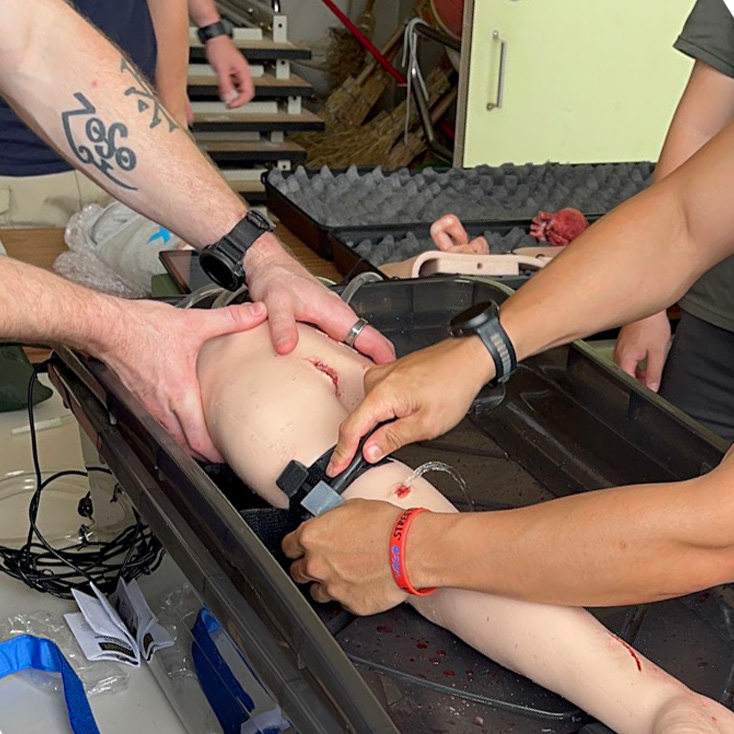
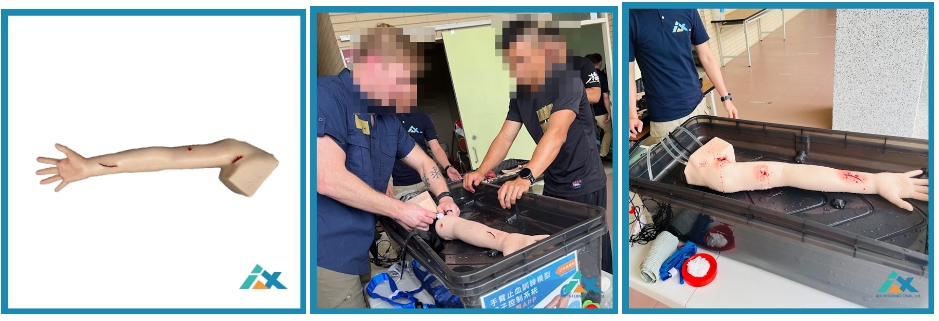
Arm Bleeding Control (three types of wounds)(link)
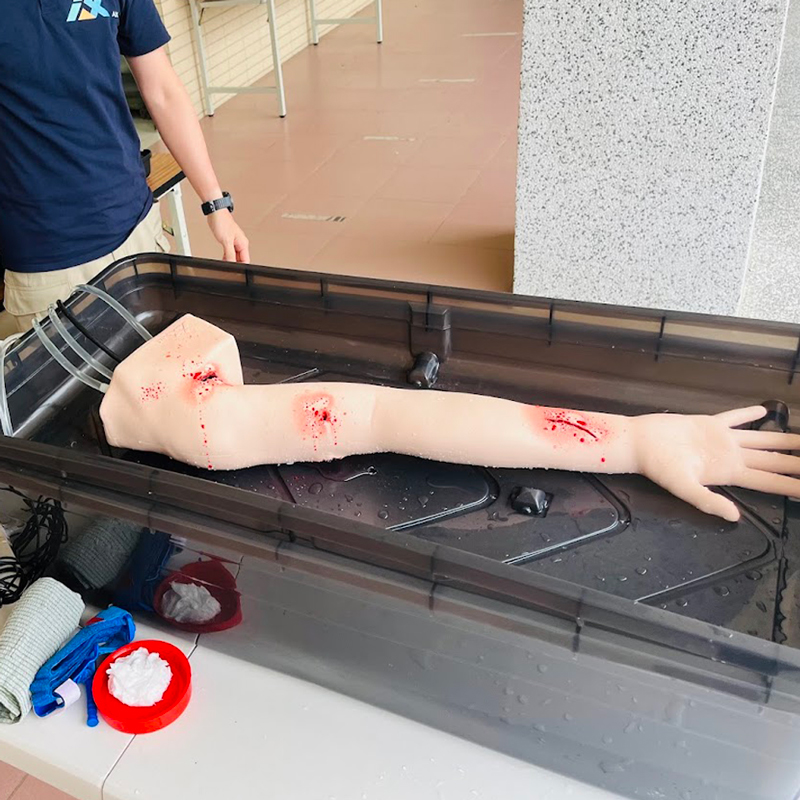

The Arm Bleeding Control training device features three different types of wounds: cuts, punctures, and lacerations. Each wound type allows for practicing different bleeding control techniques: applying pressure, using a tourniquet, and packing the wound.
The design of the Arm Bleeding Control device makes bleeding control training more challenging than stopping bleeding on a real person. This is because everyone's body structure varies, requiring different amounts of pressure for effective control. Successfully stopping bleeding on this device indicates that the techniques will also be effective on real patients. Below are detailed data explanations.
Generally, in bleeding control training, narrower blood vessels are easier to control, and softer skin makes tourniquet application simpler. According to medical data, the average person's arterial blood vessel diameter ranges from 2.5 to 3.5 cm, while the Arm Bleeding Control device features blood vessels with a diameter of approximately 6 cm. Additionally, the softness of human skin typically measures 0.1 to 0.2 on the Shore A hardness scale, whereas the Arm Bleeding Control device's skin measures 20 on the Shore A hardness scale.
These design choices are why the Arm Bleeding Control device presents a higher difficulty level. By providing a more challenging training environment, trainees can develop stronger and more precise bleeding control skills. This ensures that once they master the techniques on this device, they will be well-prepared to apply them effectively in real-life scenarios.
The three wound types—cuts, punctures, and lacerations—each present unique challenges. Cuts require sustained direct pressure to control bleeding, punctures necessitate the use of tourniquets to stop arterial flow, and lacerations need thorough packing with gauze to ensure all bleeding points are controlled. By training on a device with enhanced difficulty, medical professionals and first responders can refine their techniques, improving their readiness and confidence in emergency situations.
In conclusion, the Arm Bleeding Control device is a comprehensive and rigorous training tool designed to prepare individuals for real-world emergency bleeding scenarios. Its challenging design ensures that those who can stop bleeding on this device will be more than capable of doing so on actual patients, thereby enhancing overall emergency response effectiveness.

More content
© rawpixel, 123RF Free Images
